In this post, we will show you how to setup local yum/dnf repository using ISO file on RHEL 9.
When RHEL 9 server is deployed in disconnected environment and don’t have internet connectivity then local yum or dnf repository becomes handy and which allow us to install packages. Local yum or dnf repository can save time and bandwidth when installing packages as we do not have download packages over the internet.
Prerequisites
- Pre-Installed RHEL 9
- RHEL 9 ISO File
- A Regular user with admin rights
Let’s deep dive into steps,
Step 1) Mount RHEL 9 ISO file
We are assuming you already have ISO file on your RHEL 9 system. Run the following mount command to mount it.
$ sudo mount -o loop rhel-baseos-9.1-x86_64-dvd.iso /mnt/
Run following commands to verify whether iso file is mounted on /mnt folder or not
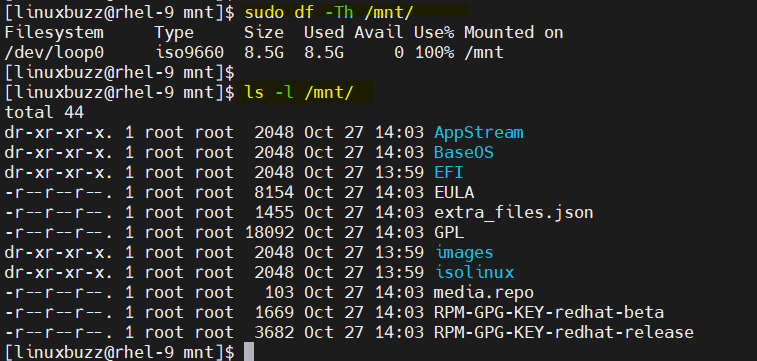
Now copy the contents of ISO file is which mounted on /mnt to /var/rhel9 folder,
$ sudo mkdir /var/rhel9 $ sudo cp -av /mnt/* /var/rhel9/
Step 2) Create a local repository file
Next, you need to create a local repository file in the “/etc/yum.repos.d” directory. This file will define the location of your local repository. Create a file with name ‘rhel9_local.repo’ with the following content.
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/rhel9_local.repo [BaseOS] name=REHL 9 - BaseOS metadata_expire=-1 gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 baseurl=file:///var/rhel9/BaseOS/ gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release [AppStream] name=RHEL 9 - AppStream metadata_expire=-1 gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 baseurl=file:///var/rhel9/AppStream/ gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release
Save and exit the file.
Step 3) Update the Package Index
After creating the repository file, you need to update the package index using the following command:
$ sudo yum clean all $ sudo yum makecache
Or, if you are using DNF:
$ sudo dnf clean all $ sudo dnf makecache
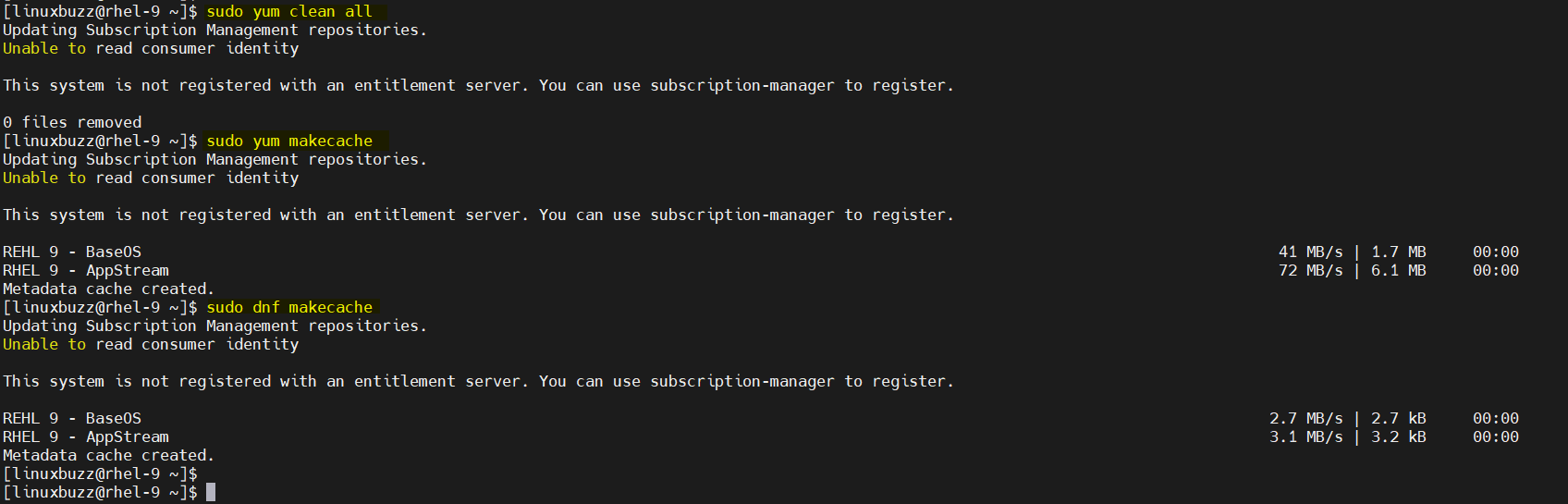
Step 4) Test Local Yum/DNF Repository
To test the local repository, run the following command:
$ sudo yum list available
Or, if you are using DNF:
$ sudo dnf list available
You should see a list of all the packages available in your local repository.
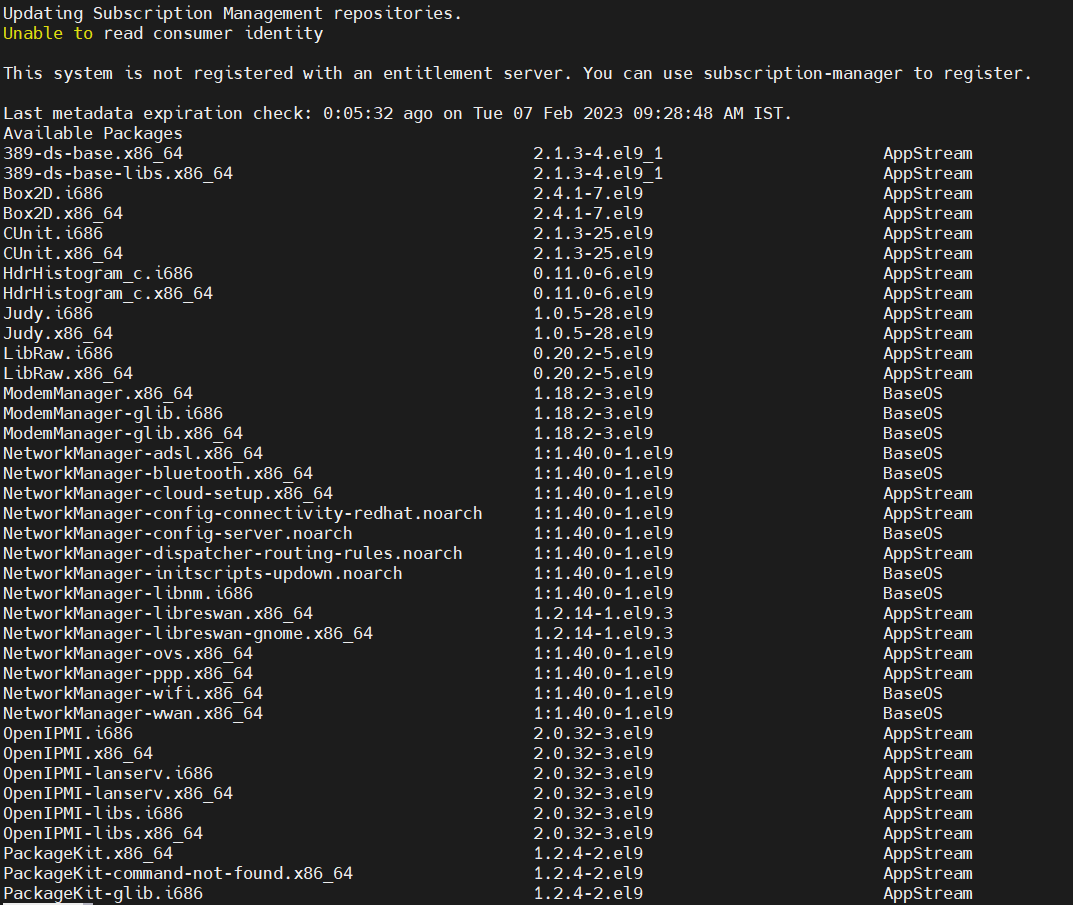
Now that you have set up your local repository, you can install packages from it. For example, to install the “nginx” package, run the following command:
$ sudo dnf install nginx
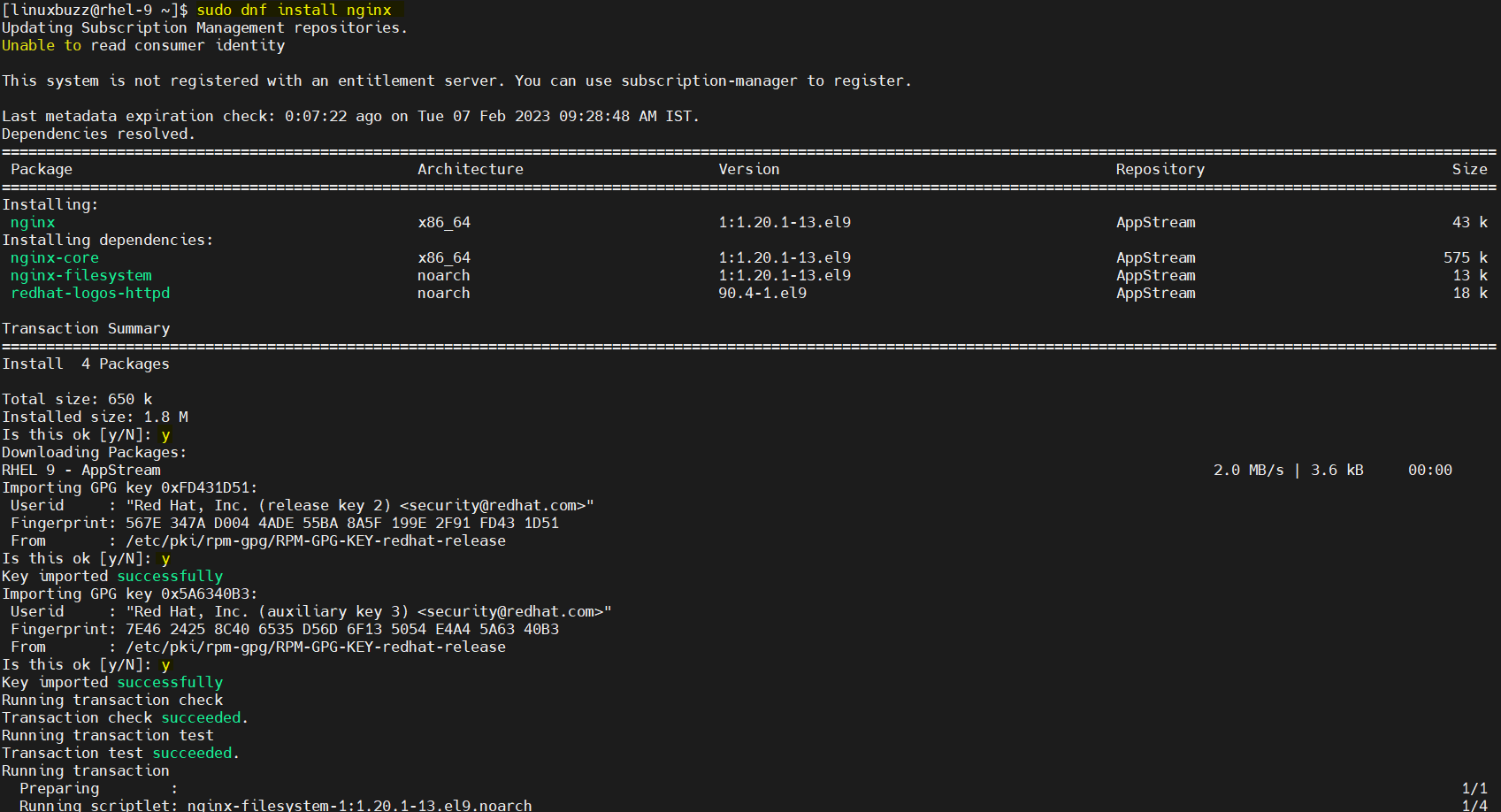
Above output confirms that nginx is installed along with its dependencies. That’s all from this post. I have you have found it informative, kindly do post your queries and feedback in below comments section.