In post, we will cover how to install minikube on Fedora 36 step by step.
Minikube is a single node local Kubernetes (k8s) cluster. If anyone is new to Kubernetes and wants to learn and explore Kubernetes, then minikube is the solution.
Minimum System Requirements for Minikube
- Minimal installed Fedora.
- Sudo User with admin rights
- 2 CPUs or more
- 2GB RAM or more
- 20GB of free disk space
- Internet connection
Without further ado, let’s jump into minikube installation steps.
Step 1) Install Docker
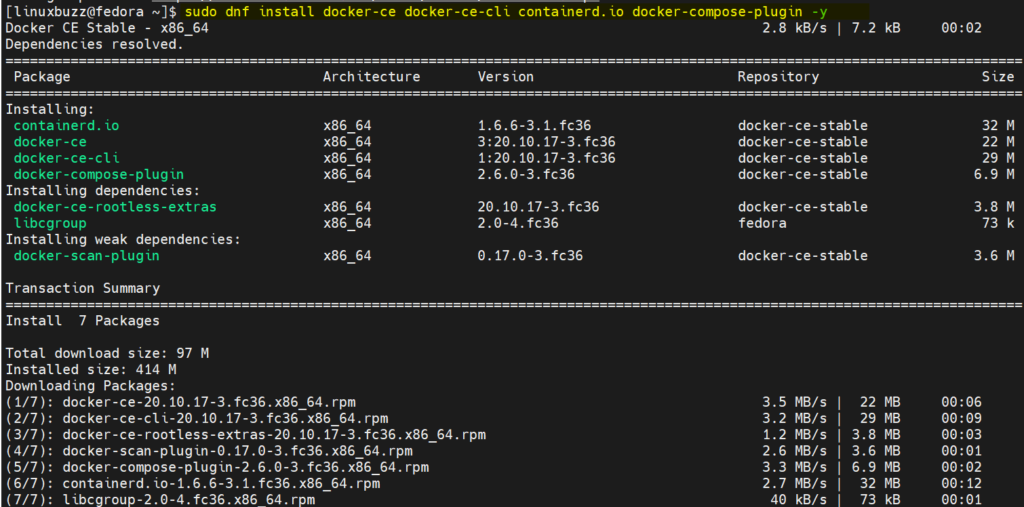
Login to the system and open the terminal, run following commands to install docker
$ sudo dnf -y install dnf-plugins-core $ sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/fedora/docker-ce.repo $ sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin -y
Start and enable docker service, run
$ sudo systemctl enable docker --now
Verify docker version, run beneath command
$ docker --version Docker version 20.10.17, build 100c701 $
Allow local user to run docker commands without sudo
$ sudo usermod -aG docker $USER $ sudo newgrp docker
Step 2) Install Latest and Stable minikube Binary
Run following commands to install latest and stable minikube binary
$ curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64 $ sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
Verify the minikube version
$ minikube version minikube version: v1.26.0 commit: f4b412861bb746be73053c9f6d2895f12cf78565 $
Step 3) Install Kubectl Utility
To interact with Kubernetes cluster, we need to install kubectl utility, run following curl command,
$ curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/`curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt`/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
Set the permissions on kubectl binary,
$ chmod +x kubectl
Move the binary to ‘/usr/local/bin’
$ sudo mv kubectl /usr/local/bin/
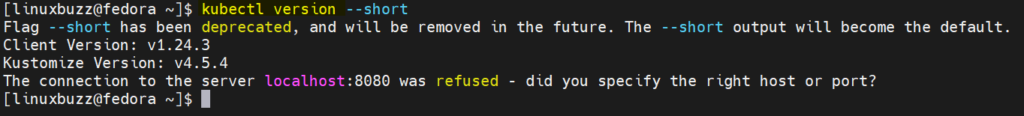
View kubectl version,
$ kubectl version --short
Output,
Step 4) Start Minikube Cluster
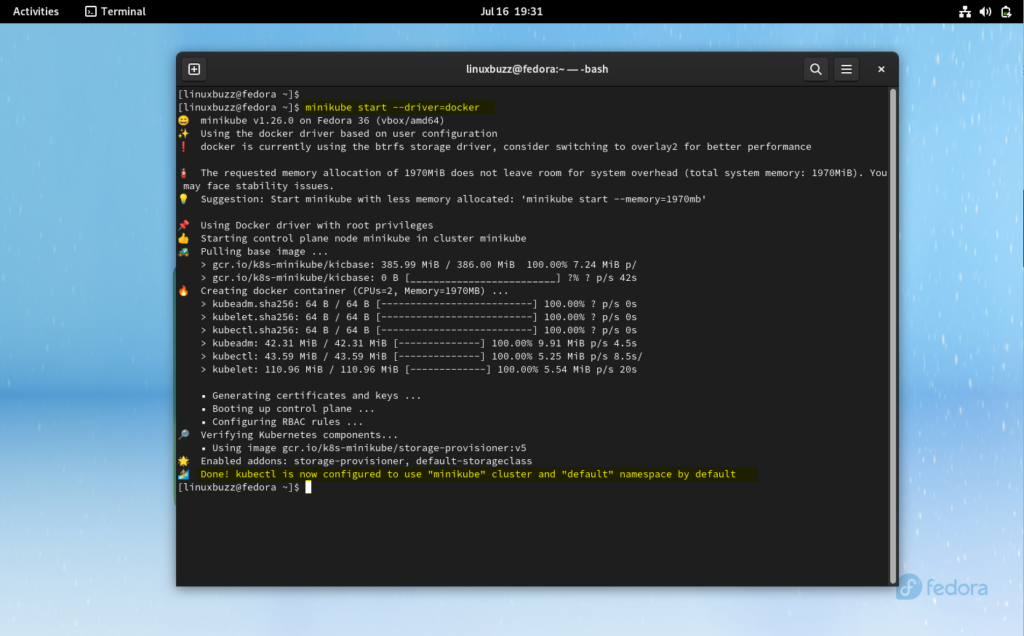
Start minikube along with docker driver, run
$ minikube start --driver=docker
Output,
Perfect, above output confirms that minikube has been started successfully.
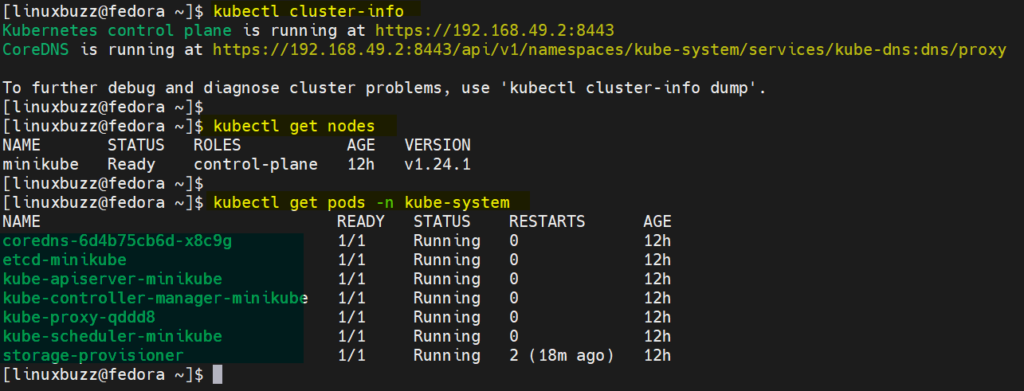
Execute following commands to view kubernetes cluster information,
$ kubectl cluster-info $ kubectl get nodes $ kubectl get pods -n kube-system
Output of above command,
Step 5) Test Kubernetes Installation
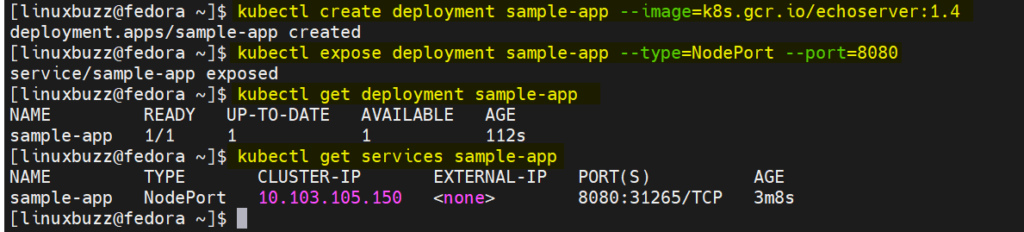
To test Kubernetes installation, we will deploy a sample application. Run beneath kubectl command,
$ kubectl create deployment sample-app --image=k8s.gcr.io/echoserver:1.4
Expose the deployment with type NodePort,
$ kubectl expose deployment sample-app --type=NodePort --port=8080
Verify deployment status,
$ kubectl get deployment sample-app $ kubectl get services sample-app
Output,
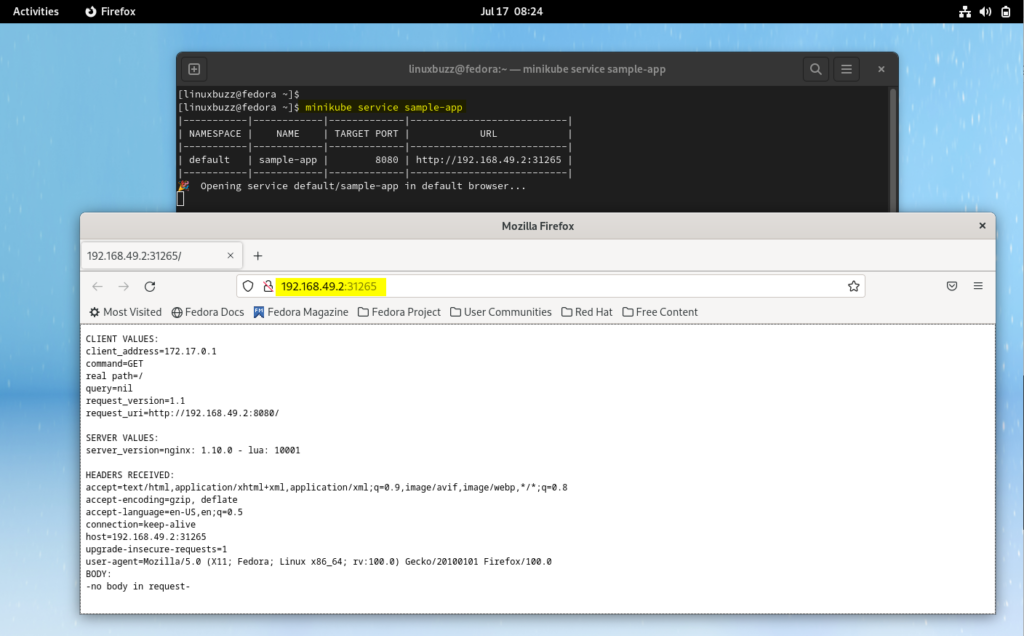
To access application, type following minikube command,
$ minikube service sample-app
It will open the application in the web browser automatically.
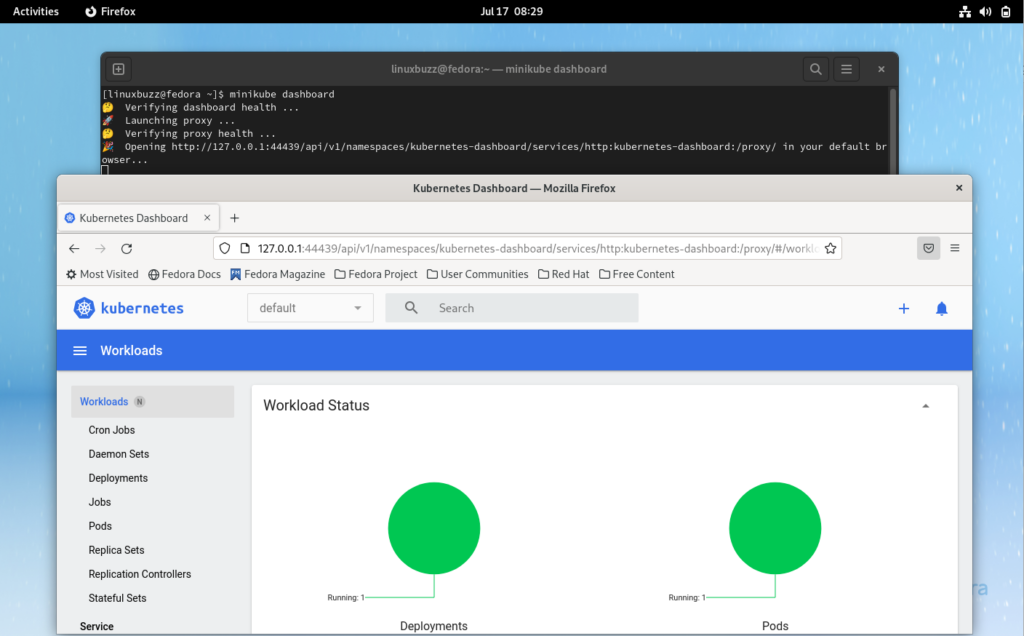
Great, above confirms that sample-app deployment is working fine. To access Kubernetes dashboard, run beneath minikube command,
$ minikube dashboard
It will automatically start Kubernetes dashboard in the web browser.
Step 6) Manage Minikube Cluster
To stop and start minikube cluster, run
$ minikube stop $ minikube start
To delete the cluster, run
$ minikube delete --all
Increase memory limit of minikube, run
$ minikube config set memory 16384 $ minikube stop $ minikube start
That’s all from this guide, I hope these steps help you to setup minikube cluster smoothly on your Fedora Linux. Your feedback and queries are most welcome.
Read Also: How to Install VirtualBox on Fedora 36